Master project management with BIM Modeling construction guide. Discover how to streamline processes and boost efficiency with expert tips.

Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of construction, effective project management is crucial for successfully completing projects within budget and on schedule.
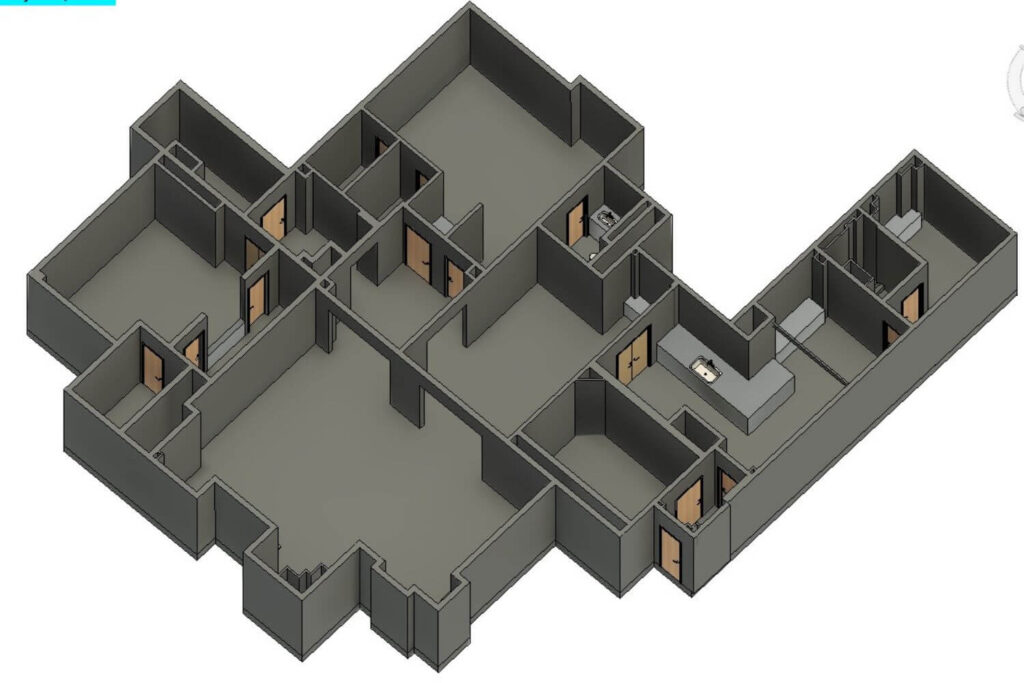
Project Management with BIM Modeling has emerged as a transformative method that revolutionizes how construction projects are planned, executed, and managed. BIM modeling provides a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building, offering an unparalleled level of detail and accuracy that traditional methods cannot match.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of Project Management with BIM modeling, starting with a deep dive into understanding the various disciplines and Levels of Development (LOD) that form the backbone of BIM modeling.
We will explore the essential tools that facilitate efficient BIM workflows, helping construction professionals select the right software for their needs.
Furthermore, we will uncover the key elements of 3D BIM modeling, highlighting how these components come together to create a cohesive and functional digital model. The practical applications of 3D BIM modeling are vast, including clash detection, enhanced collaboration, facilities management, and precise cost estimation, all of which will be discussed in detail.
Implementing BIM Project Management requires a strategic approach, and we will provide a step-by-step guide on effectively integrating BIM into your construction processes.
Lastly, we will discuss the advantages of outsourcing BIM modeling to specialized consulting companies, emphasizing how this can enhance project outcomes and streamline operations.
United States
(+1) 757 656 3274
United Kingdom
(+44) 7360 267087
Understanding Project Management with BIM Modeling
What is Project Management with BIM Modeling
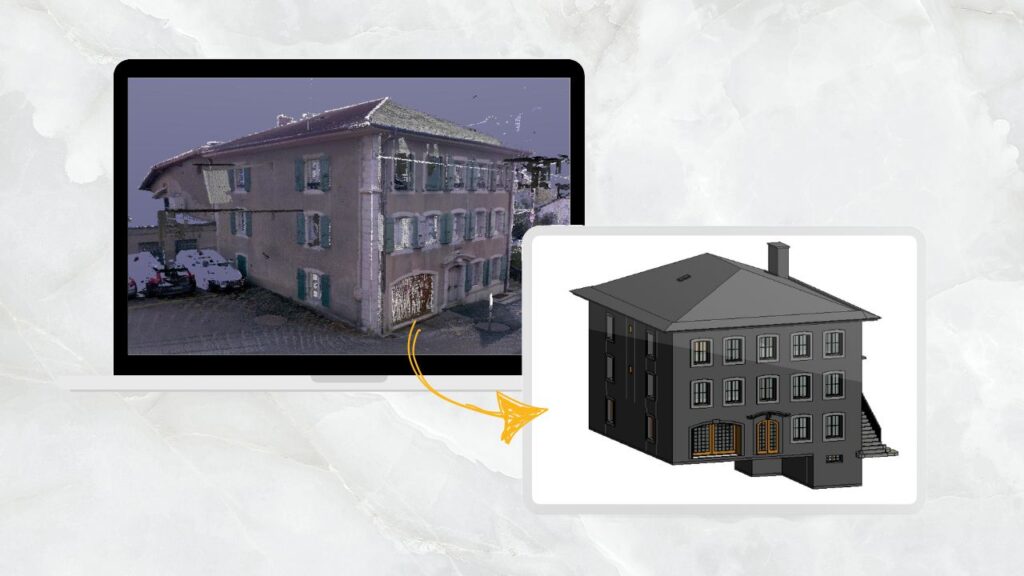
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility.
BIM is not just a software but a process involving the generation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places.
Project Management with BIM modeling integrates multi-disciplinary data to create detailed three-dimensional models in different disciplines that serve as a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility, forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life cycle, from the earliest conception to demolition .
Disciplines of BIM Modeling
BIM modeling involves various disciplines, each contributing unique aspects to the overall project model:
- Architectural BIM: Focuses on the design, visualization, and documentation of buildings, encompassing aspects like spatial relationships, geometry, and aesthetics.
- Structural BIM: Deals with the design and analysis of the structural elements of a building, ensuring stability and integrity.
- MEP BIM: Covers the design and coordination of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within the building.
- Civil BIM: Involves site planning, earthwork, and infrastructure design, integrating the building with its surrounding environment.
- Construction Management BIM: Focuses on planning, coordination, and execution of construction activities, and overall project management with BIM modeling.
Different LODs in BIM Modeling

Levels of Development (LOD) in BIM modeling refer to the various stages of detail and accuracy of the building model as it progresses through its lifecycle.
These levels are standardized to ensure consistency and clarity in the information shared among stakeholders for effective project management with BIM modeling.
The common LODs are:
- LOD 100 (Conceptual): Basic overall building massing, with approximate area, height, volume, location, and orientation.
- LOD 200 (Schematic Design): Generalized representation with approximate quantities, size, shape, location, and orientation. Basic details such as wall thicknesses and structural systems are included.
- LOD 300 (Detailed Design): Precise geometry and location, size, shape, quantity, and orientation. Elements are accurate and detailed enough for construction documentation.
- LOD 350 (Construction Documentation): Includes connections between building elements and shows how various systems fit together.
- LOD 400 (Fabrication and Assembly): Detailed enough for fabrication, including specific detailing, dimensions, and finishes. Models are used directly for manufacturing.
- LOD 500 (As-Built): Represents the final constructed conditions, capturing exact dimensions, locations, quantities, and configurations. This level is used for facilities management and operations.
These LODs help in project management with BIM modeling by progressively adding detail, ensuring that all stakeholders have the appropriate level of information at each stage of the project.
Get FREE Quote
For BIM Services for Your Project
Tools for Project Management with BIM Modeling



Effective project management in construction often relies on a suite of powerful tools that facilitate collaboration, precision, and efficiency.
Autodesk provides several industry-leading products that integrate seamlessly with BIM workflows, helping project managers and teams achieve successful outcomes.
Here’s a look at how key Autodesk tools like AutoCAD, Revit, BIM Collaborate Pro, and Navisworks contribute to superior project management in BIM modeling.
1. AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a versatile CAD software widely used for creating detailed 2D and 3D designs. In the context of BIM:
- Design and Drafting: AutoCAD allows for the precise drafting of architectural plans, which can then be integrated into BIM models. Its robust toolset enables the creation of accurate blueprints that form the foundation of any construction project.
- Integration: AutoCAD files can be imported into Revit and other BIM software, ensuring that initial designs and drawings are seamlessly integrated into the broader BIM environment.
- Customization and Automation: AutoCAD’s extensive customization options and scripting capabilities allow for the automation of repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors.
2. Revit
Revit is Autodesk’s flagship BIM software designed for architects, engineers, and construction professionals for effective project management with BIM modeling:
- Parametric Modeling: Revit supports parametric modeling, where changes to one part of the model automatically update related components, ensuring consistency and reducing manual adjustments.
- Multi-Disciplinary Collaboration: Revit facilitates collaboration across various disciplines (architectural, structural, MEP), enabling all stakeholders to work on a unified model, enhancing coordination and communication.
- Documentation: It generates comprehensive construction documents, including plans, sections, elevations, and schedules, directly from the BIM model, ensuring accuracy and coherence throughout the project lifecycle.
3. BIM Collaborate Pro
BIM Collaborate Pro (formerly BIM 360 Design) is a cloud-based collaboration tool that enhances project management with BIM modeling and team coordination:
- Centralized Data: It provides a common data environment where all project information is stored, ensuring that everyone has access to the most up-to-date data.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Teams can work together in real-time on shared Revit models, reducing delays and enhancing decision-making processes.
- Issue Tracking and Management: BIM Collaborate Pro allows for the identification, assignment, and tracking of issues within the BIM model, helping to manage and resolve problems efficiently.
Practical Applications of 3D BIM Mmodeling
1. Clash Detection
Clash Detection is a critical application of Project management with BIM modeling that identifies conflicts between different building systems before construction begins.
These clashes can occur between structural elements, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems, and other components within a project.
Here’s how project management with BIM modeling facilitates effective clash detection:
Automatic Clash Detection
BIM software like Navisworks can automatically detect clashes by comparing different models, such as architectural, structural, and MEP.
This automated process ensures that potential conflicts are identified early, reducing the risk of costly changes during construction.
Visualization and Resolution
The 3D visualization capabilities of BIM allow project teams to see where clashes occur, making it easier to understand and resolve these issues.
Teams can then adjust the design to mitigate these clashes, ensuring a smoother construction process.
Cost and Time Savings
By identifying and resolving clashes during the design phase, BIM significantly reduces the likelihood of rework, change orders, and project delays. This proactive approach leads to substantial cost and time savings.
2. Cost Estimation
Automated Quantity Take-offs
BIM software excels in generating precise quantity takeoffs directly from 3D models. This feature extracts detailed data on materials and components, ensuring that cost estimations are based on accurate quantities.
This automation streamlines the estimation process, reducing manual errors and saving time.
Real-Time Cost Integration
With BIM tools, cost databases can be integrated with the model, enabling real-time cost calculations.
As the design evolves, any changes instantly reflect their cost implications. This dynamic adjustment facilitates better financial planning and control, allowing project managers to make informed decisions quickly.
Detailed Cost Breakdown
Project management with BIM modeling provides a comprehensive breakdown of costs for various project elements.
This detailed view helps stakeholders understand where money is being allocated and highlights potential areas for cost savings. It ensures transparency and aids in managing the budget more effectively.
Scenario Analysis
BIM’s ability to simulate various scenarios allows project managers to evaluate different design options and their financial impacts.
By comparing these scenarios, teams can make well-informed decisions that balance quality, cost, and timelines, optimizing project outcomes.
Facilities Management
Facilities Management with BIM Modeling involves maintaining and managing a building’s systems and services to ensure they operate efficiently.
BIM plays a significant role in enhancing facilities management through:
Comprehensive Data Repository
Project management with BIM serves as a robust digital archive, documenting every detail of a building’s components and systems.
For facilities managers, this comprehensive data repository is a treasure trove of information, providing deep insights into the building’s design, construction, and ongoing operations.
This detailed record-keeping supports informed decision-making and efficient management practices.
Maintenance Scheduling
One of the standout features of facilities management with BIM modeling is its ability to incorporate maintenance schedules for all building systems.
Facilities managers can leverage this capability to plan and execute regular maintenance activities meticulously, ensuring that all systems remain operational and efficient.
This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends the life of building components.
Asset Management
Using facilities management with BIM modeling, every element of the building, from structural components to MEP systems, is meticulously documented.
This includes critical details such as manufacturer information, installation dates, and maintenance history.
Such detailed asset documentation facilitates superior lifecycle management and informed decision-making regarding repairs, replacements, and upgrades.
Energy Management
Integrating project management with BIM modeling for building management systems allows for precise monitoring and management of energy consumption.
Facilities managers can use this data to optimize energy usage, implement sustainability practices, and reduce operational costs.
Effective energy management not only lowers expenses but also promotes environmental sustainability.
Get FREE Quote
For BIM Services for Your Project
Choosing between In-House and Outsourcing BIM for Project Management?
Implementing 3D BIM modeling on a construction project involves strategic planning, allocation of resources, and choosing between in-house capabilities or outsourcing to specialized firms.
Both approaches have their own set of advantages and challenges. Here’s a detailed comparison to help you decide which method suits your project needs best:
| Aspect | In-House BIM Capabilities | Outsourcing BIM |
|---|---|---|
Initial Setup Cost | High: Requires investment in software and training | Low/Moderate: Cost depends on the scope and duration of the project |
Control and Customization | High: Direct control over processes and customization to specific needs | Moderate: Customization available but within the limits of the outsourcing agreement |
Expertise and Skillset | Variable: Dependent on the existing skill level of the team | High: Access to specialized skills and extensive experience |
Scalability | Limited: Scaling up requires hiring and training new staff | High: Easily scalable by engaging more resources from the outsourcing partner |
Turnaround Time | Variable: Can be slower if the team is less experienced | Typically Faster: Specialized firms often have streamlined processes and greater efficiency |
Quality Control | High: Direct oversight and quality control | High: Reputable firms have established quality assurance processes |
Cost Over Time | Potentially Lower: Long-term cost savings if the team is fully utilized | Potentially Higher: Continuous costs based on the scope of work and duration |
Technology Upgrades | High Cost: Frequent updates and training required | Low Cost: Outsourcing firms typically stay up-to-date with the latest technology |
How to Implement 3D BIM Modeling for Project Management
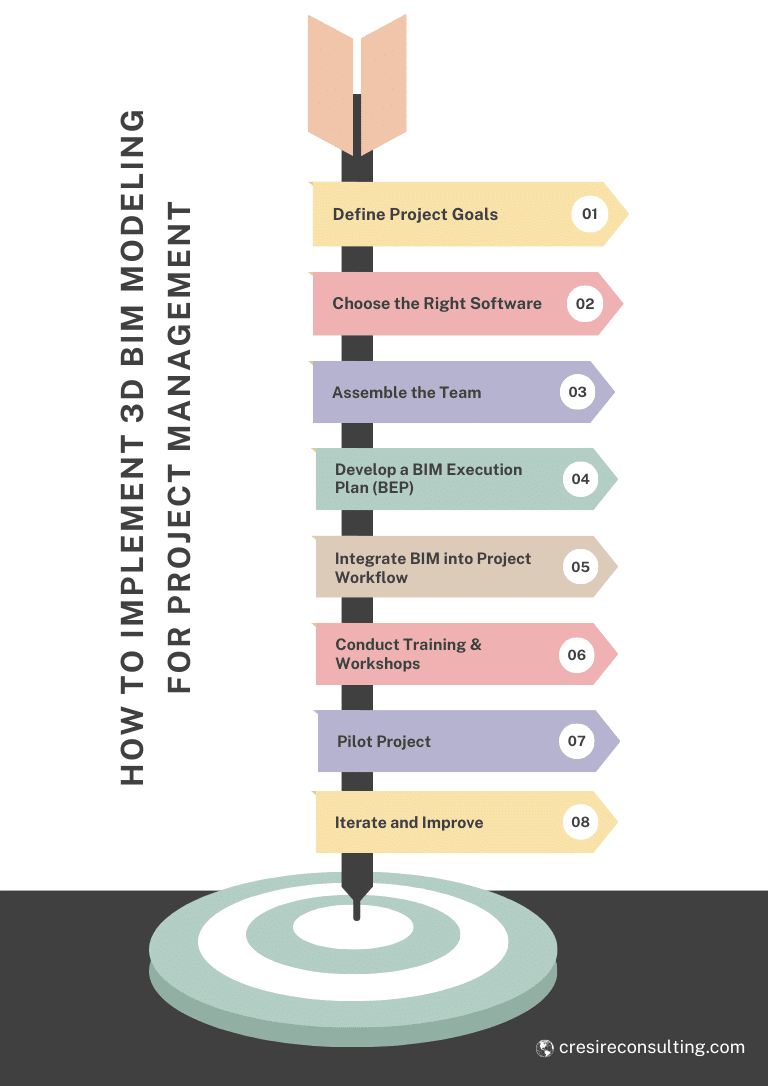
1. Define Project Goals
Clearly outline the objectives and expected outcomes of implementing 3D BIM modeling for your project. This includes defining the scope, deliverables, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
2. Choose the Right Software
Select appropriate BIM software that aligns with your project needs. Commonly used software includes Autodesk Revit for modeling, Navisworks for clash detection, and BIM 360 for collaboration.
3. Assemble the Team
Depending on whether you are implementing in-house or outsourcing, gather a team of skilled professionals. For in-house, this involves hiring or training staff. For outsourcing, choose a reliable BIM service provider with a proven track record.
4. Develop a BIM Execution Plan (BEP)
Create a detailed plan that outlines BIM processes, standards, roles, responsibilities, and workflows for effective Project Management with BIM Modeling. This ensures all stakeholders are aligned and understand their tasks.
5. Integrate BIM into Project Workflow
Incorporate BIM modeling into your existing project management processes. This involves setting up communication channels, integrating BIM with other project management tools, and ensuring seamless data flow.
6. Conduct Training and Workshops
If implementing in-house, provide comprehensive training for your team on the selected BIM tools and processes.
For outsourcing, ensure the service provider understands your project requirements through detailed briefings and workshops.
7. Pilot Project
Start with a pilot project to test the BIM implementation strategy. This allows you to identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments before full-scale deployment.
8. Iterate and Improve
Use feedback and performance data to refine and improve the BIM implementation process. Continuous improvement ensures that the BIM adoption remains effective and efficient.
By carefully considering these factors and following these steps, you can successfully implement 3D BIM modeling in your construction project, whether you choose to develop in-house capabilities or outsource to a specialized firm.
This strategic approach ensures that you leverage the full benefits of BIM, leading to enhanced project management, improved collaboration, and better project outcomes.
Conclusion
Mastering project management with BIM modeling is essential for AEC professionals in the USA, UK, Australia, Italy, and Germany.
This comprehensive guide has shown how BIM transforms modern construction by enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration.
Understanding the disciplines and Levels of Detail (LOD) in BIM lays the groundwork for effective project execution.
With tools like Revit, Navisworks, and BIM Collaborate Pro, teams can seamlessly visualize, plan, and coordinate their projects. Key elements of 3D BIM modeling, such as parametric design and data integration, drive successful project outcomes.
Practical applications like clash detection, cost estimation, and facilities management highlight BIM’s capability to prevent issues, control costs, and manage assets efficiently. Implementing BIM involves strategic planning.
Whether you build in-house capabilities or outsource to specialized firms, each option offers unique benefits. Outsourcing can provide access to the latest technology and expert skills, ensuring high-quality project delivery.
In conclusion, embracing BIM in Project Management transforms how construction projects are managed. It fosters better collaboration, reduces errors, and improves overall efficiency.
By integrating BIM practices, AEC professionals can confidently tackle modern construction challenges, delivering projects on time, within budget, and to the highest standards. The journey to mastering BIM is ongoing, but the benefits it offers are substantial and well worth the effort.
Related Posts
Our Recent Projects on BIM Services
Share Via
Tags

Devashish Sharma
Devashish is Founder/Director at Cresire where he leads BIM services. He holds a bachelor’s degree in Civil Engineering from the University of Sheffield and an MSc in Construction Project Management from The University of the West of England. His vision behind CRESIRE is to provide BIM services, adhering to best practices and procedures, to global customers, helping customers to save extensive production costs and overruns.